Female reproductive system
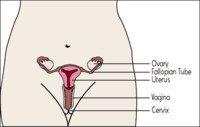
A woman’s reproductive system includes the clitoris, vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, cervix, and breasts. While we can think of these parts in relation to pregnancy, they also can produce sexual pleasure. Areas of the body that can produce feelings of sexual pleasure when touched are referred to as erogenous zones.
- Clitoris: The clitoris is an area just above the urethra. This area is very sensitive and is a major erogenous zone.
- Vagina: The opening of the vagina is located between the urethra and the anus. The vagina is a muscular tube that stretches allowing the penis to enter during sexual intercourse. It also acts as the birth canal during the birth process.
- Cervix: The cervix is the opening to the uterus. It has also been reported to affect the sexual response.
- Uterus: The uterus or womb is located in the lower abdomen. It is a muscular organ that can expand. Its purpose is to provide a good environment for a growing unborn baby.
- Ovaries: The ovaries are two small organs, located on each side of the uterus. The ovaries house the eggs, that when fertilized, develop into a baby. Each month, the ovaries release at least one egg. The ovaries also release hormones to allow for your sexual drive.
- Fallopian tubes: The fallopian tubes are tubes that carry the egg from the ovary to the uterus. Sperm travel from the vagina to the fallopian tubes to fertilize an egg. A fertilized egg will travel to the uterus and grow into a baby. An unfertilized egg will exit the body during the monthly menstrual period. The fallopian tubes do not affect sexual response but do play a role in becoming pregnant.
- Breasts: While the female breasts provide a newborn with nutrition in the form of breast milk, the breasts also have sensitive tissue that can produce sexual pleasure.
Female sexuality and spinal cord injury
Spinal cord injury (SCI) can affect female sexuality in a range of ways.
- Fertility: The ability to become pregnant and give birth is usually not affected by a spinal cord injury. On an average, a female will miss about 3 menstrual periods after a SCI. Some may miss a few more periods and some may not miss any periods. The menstrual cycle will almost always return to normal. However, it is important to remember that it is possible to become pregnant before the cycle returns to normal. So if you do not want to become pregnant, use a reliable method of birth control.
- Pregnancy: Choose a doctor who is familiar with SCI and pregnancy or is willing to learn. It is important to let a doctor check your overall health before getting pregnant. Your bladder and kidneys will need to be monitored while you are pregnant.
- The opening to the womb may be thin and result in an early delivery, though most women with SCI have vaginal deliveries.
- If a woman’s injury is at the T6 or above level, she may have problems with autonomic dysreflexia. Special measures should be taken during labor and delivery to prevent this.
- If your injury is above the T10 level, you may not feel labor pains. But you will need to know when labor starts. You can wear a special monitor, especially at night that will let you know when labor has started. Be sure to talk about this with your doctor.
- Birth control: The best choice to prevent pregnancy is a combination of methods.
- Condoms used with spermicide foam or a diaphragm used with spermicide cream are two common methods. Please note that animal-skin condoms do not prevent against sexually transmitted diseases such as HIV/AIDS.
- Birth control pills can be a problem because they may cause blood clots. Often if a woman has had no problems with blood clots, she may be able to take a low-dose pill. Many women are able to take birth control pills after their discharge from rehab, so check with your doctor to see which option is best for you.
- Some women who have no plans to get pregnant may choose to have a tubal ligation.
- Orgasm: If feeling in the muscles below the navel is absent, orgasm will probably not occur, however, the pleasure leading up to and after an orgasm is likely to remain. One out of five women can orgasm with a cervical stimulator.
- Lubrication: SCI usually stops the body’s ability to lubricate during sexual arousal. This is easily corrected by the use of lubricants such as Astroglide and KY jelly. Do not use lubricants with oil in them. It should be applied while touching and every 3 minutes during any sexual activity that includes touch other than oral sex. After oral sex, you will need to apply it again if having intercourse. Always use a lubricant unless your doctor tells you it is not necessary.
- Indwelling catheter: If you have an indwelling catheter, coat it well with KY Jelly and tape it to your left or right side before having sex.
- Intermittent catheterization: Be sure to empty your bladder before and after having sexual intercourse. Limit amount of caffeine and alcohol before sex as it may cause urinary leakage. Good hygiene before and after sexual intercourse will help prevent a bladder infection.
- Bowel program: Wait two hours after finishing your bowel program before having sex. If the person who does your bowel program is also your sex partner, do not talk about sex during your bowel program. Talk about other topics instead.
- Sexual positions: “Anything you can do, you can do.” Act safely to prevent falls, but otherwise sexual positions are up to you.
