Learn About the Anatomy of the Brain and How Each Part Functions
Obtaining a general understanding of the brain and its functions is important to understanding the rehabilitation process. There are three major parts of the brain:
- cerebrum
- brain stem
- cerebellum
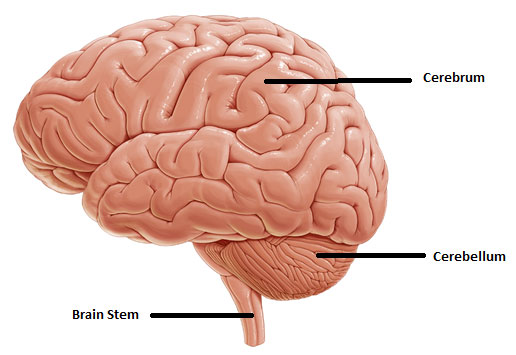
The cerebrum is made up an outer layer, called the cortex, which is responsible for thinking, learning, memory, and emotions. Additionally, there are deeper, inner structures of the cerebrum, such as the thalamus, a small structure located slightly above the brainstem. This is the gateway for most of the sensory pathways. The thalamus plays a role in regulating awareness and emotional aspects of sensory experiences (For example: reaction to fear or hunger).
The brain stem begins underneath the brain and extends downward until it becomes part of the spinal cord. It is very important because it handles automatic functions like breathing, heart rate, and wakefulness. The reticular activating system is the part of the brain stem that responsible for wakefulness. This is a collection of neurons, located in the upper brain stem, that projects to and stimulates the areas of the cortex that is responsible for awareness—the ability to think and perceive.
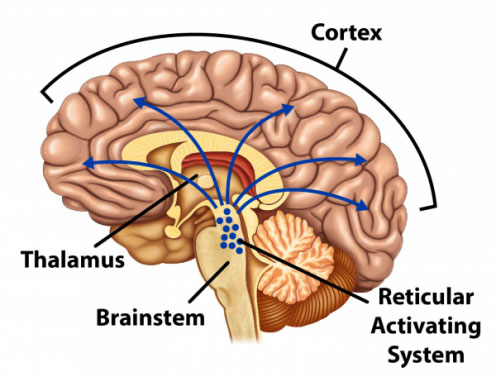
Consciousness requires both wakefulness and awareness. As you just learned, the parts of the brain that are responsible for wakefulness are located in a different area than the parts responsible for awareness. Disorders of consciousness are a result of either damage to one or both areas of the brain or damage to the connective network of neurons linking the areas responsible for wakefulness and awareness.


